📋 Executive Summary
This document provides comprehensive preparation for a nephrology roundtable discussion on heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) as a fundamentally renal disease. Key themes include:
🔬 Pathophysiology
The central role of the kidney in HFpEF pathogenesis through MR overactivation, galectin-3 mediation, and hemodynamic interactions
📊 CKM Framework
The emerging cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome framework integrated with KDIGO staging
💊 GDMT Evidence
Guideline-directed medical therapy evidence including FINEARTS-HF and CONFIDENCE
🩺 Clinical Implementation
Practical strategies and positioning of finerenone across the HFpEF spectrum
📑 Table of Contents
- Part I: Pathophysiological Framework
- HFpEF as Fundamentally Renal Disease
- Galectin-3: Molecular Mediator of Cardiorenal Fibrosis
- Albuminuria as Cardiovascular Risk Indicator
- HFpEF Phenomapping: The CKD-Dominant Phenotype
- Part II: Integrated KDIGO Heat Map
- Interactive CKM-KDIGO Risk Heat Map
- Albuminuria: The Dominant Driver of Risk
- Part III: CKM Syndrome Framework
- Expanded CKM Staging with KDIGO Integration
- Therapeutic Implications by CKM Stage
- Part IV: GDMT Evidence
- SGLT2 Inhibitors: Class I, Level A for HFpEF
- Finerenone: FINEARTS-HF and FIDELITY
- Finerenone vs Steroidal MRAs
- Part V: Clinical Implementation
- ⭐ CONFIDENCE Trial: Simultaneous Initiation (HIGHLIGHTED)
- HFpEF Screening in Nephrology Practice
- Finerenone Dosing and Monitoring
- Part VI: Roundtable Q&A
- Prepared Responses to Discussion Questions
- Appendix
- Key Clinical Pearls
Part I: HFpEF as Fundamentally Renal Disease
🔬 The Paulus-Tschöpe Paradigm
The Paulus-Tschöpe paradigm establishes comorbidity-driven coronary microvascular endothelial inflammation—rather than ischemic cardiomyocyte death—as the central mechanism of HFpEF.
The Mechanism Chain:
Comorbidities → IL-6, TNF-α, CRP → Endothelial dysfunction → ↓NO/cGMP → Titin hypophosphorylation → Diastolic dysfunction
🫘 The Kidney's Central Role
1. MR Overactivation
Mineralocorticoid receptor overactivation occurs simultaneously in cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and immune cells, stimulating TGF-β, IL-6, and PAI-1 production.
2. Galectin-3 Mediation
Galectin-3 functions as a bidirectional mediator linking kidney injury to cardiac fibrosis. It amplifies TGF-β signaling by stabilizing TGFBR2.
3. Hemodynamic Interactions
A self-perpetuating cycle: reduced GFR → ↓sodium filtration → RAAS activation → volume expansion → hypertension → LVH → elevated CVP → "renal tamponade" → ↓GFR
🧬 Galectin-3: The Molecular Bridge
Molecular Architecture
Galectin-3 is a 30-kDa protein encoded by the LGALS3 gene—the only chimeric member of the galectin family. It consists of:
The Adoptive Transfer Evidence
2025 Mechanistic Update
Recent research has elucidated the molecular mechanism: extracellular galectin-3 binds directly to TGF-β receptor 2 (TGFBR2) through its CRD, inhibiting receptor ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation—prolonging receptor half-life and amplifying TGF-β signaling.
Clinical Correlations
Correlation between reduced GFR and elevated galectin-3
Galectin-3 predicts type 1 cardiorenal syndrome
Per doubling of galectin-3 levels (FDA validated)
📈 Albuminuria as Cardiovascular Risk Indicator
Albuminuria serves as both a kidney injury marker and an independent cardiovascular risk indicator, reflecting systemic endothelial injury affecting both the glomerular barrier and coronary microcirculation.
ARIC Study Evidence (n=10,975)
Continuous graded relationship even within "normal" range:
| UACR Category | HF Hazard Ratio |
|---|---|
| Optimal (<5 mg/g) | Reference |
| Intermediate-normal (5-9 mg/g) | HR 1.54 |
| High-normal (10-29 mg/g) | HR 1.91 |
| Microalbuminuria (30-299 mg/g) | HR 2.49 |
| Macroalbuminuria (≥300 mg/g) | HR 3.47 |
Each doubling of UACR = 15% increased HF risk (HR 1.15), independent of eGFR
CHARM HFpEF Subset
(95% CI 1.21-1.69, p<0.0001)
(95% CI 1.39-2.20, p<0.0001)
🗺️ HFpEF Phenomapping: The CKD-Dominant Phenotype
Shah Phenogroups (Circulation 2016)
Hierarchical clustering on 397 HFpEF patients using 67 phenotypic variables identified three distinct phenogroups:
Phenogroup 3: CKD-Dominant (Highest Risk)
- Older age (median 75 years)
- CKD as defining feature
- 43% atrial fibrillation
- Pulmonary hypertension
- RV dysfunction
- Overt diastolic dysfunction
(95% CI 2.0-9.1, p<0.001)
for HF hospitalization vs other phenogroups
Part II: Interactive CKM-KDIGO Risk Heat Map
🎯 Integrated KDIGO-CKM Risk Stratification: The Visual Guide
This interactive heat map combines KDIGO CKD staging with AHA CKM syndrome classification. Click any cell to see detailed risk profiles and therapeutic recommendations.
Critical insight: Albuminuria is the dominant driver of cardiovascular risk—often more predictive than eGFR decline alone. A patient with eGFR 85 and UACR 400 faces higher CV risk than one with eGFR 35 and UACR 15.
| Albuminuria Categories (UACR mg/g) — PRIMARY RISK DRIVER | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
A1
<30
Normal-mild
|
A2
30-300
Mod increased
|
A3
>300
Severely increased
|
||
Risk Profile
Therapeutic Recommendations
🎨 Risk Color Legend
⚠️ Albuminuria Dominance: The Key Insight
• G1A3 (eGFR ≥90, UACR >300): HF risk 3.47× — similar to G3b/A1!
• CKD progression steepens MORE across A categories than G categories
• CV risk exceeds kidney failure risk in early albuminuric CKD
• eGFR <30 = automatic CV risk equivalent regardless of UACR
⚠️ Albuminuria: The Dominant Driver of Risk Progression
The Critical Principle:
Albuminuria is a more powerful predictor of adverse outcomes than eGFR decline, and the risk gradient steepens dramatically with increasing albuminuria severity.
The Clinical Comparison
Patient A
eGFR 85 mL/min/1.73m² + UACR 400 mg/g
(G2A3)
HIGHER CV risk despite excellent eGFR
Patient B
eGFR 35 mL/min/1.73m² + UACR 15 mg/g
(G3bA1)
LOWER CV risk despite poor eGFR
The Albuminuria Paradox
In adults with albuminuria and preserved eGFR, the absolute risk of cardiovascular events substantially exceeds the risk of progressing to dialysis. A patient with eGFR 75 and UACR 200 faces low short-term risk of kidney failure but substantially elevated cardiovascular risk.
Reframe the conversation: In early-stage albuminuric CKD, we are primarily preventing cardiovascular events, with kidney protection as an important co-benefit.
Part III: CKM Syndrome Framework
📋 AHA Presidential Advisory (2023)
CKM syndrome is defined as a "systemic disorder with pathophysiological interactions among metabolic risk factors, CKD, and cardiovascular system leading to multiorgan dysfunction and high adverse cardiovascular outcomes."
🖼️ CKM Staging Framework (AHA 2023)
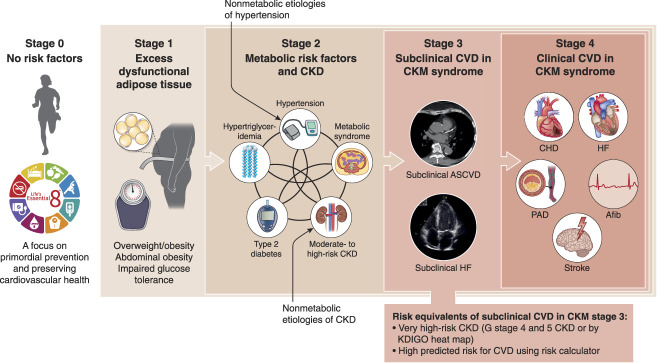
Figure 1: Stages of the American Heart Association CKM Health Syndrome.
Source: Bansal N, Weiner D, Sarnak M. JASN 2024;35(5):649-652. PMC11149035
🔢 CKM Staging with KDIGO Integration
Stage 0-1: No/Low Risk
KDIGO: G1-G2/A1 without metabolic disease
Action: Lifestyle modification, annual screening
Screen: UACR even at Stage 1 (adiposity)
Stage 2: Metabolic Risk or Mod-High CKD
KDIGO: G3a/A1, G1-G2/A2-A3, or metabolic risk factors
Key insight: Stage 2 can be triggered by albuminuria alone
Action: SGLT2i (eGFR ≥20), optimize RAASi, consider finerenone
Stage 3: CV Risk Equivalent
KDIGO: G4-G5 (any albuminuria), G3a-G3b/A3, or PREVENT ≥20%
Critical: eGFR <30 = automatic CKM Stage 3
Action: All four pillars, cardiology referral
Stage 4: Clinical CVD + CKM
4a: CKD without ESKD
4b: ESKD (10-20× mortality vs general population)
Action: Multidisciplinary, maximize tolerated therapy, RRT planning
Part IV: Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy Evidence
💊 SGLT2 Inhibitors: Class I, Level A for HFpEF
EMPEROR-Preserved (n=5,988)
Empagliflozin vs placebo in LVEF >40%
Primary endpoint (CV death + HF hospitalization):
NNT = 30 over 26.2 months
Benefit consistent regardless of diabetes status
DELIVER (n=6,263)
Dapagliflozin vs placebo in LVEF >40%
Primary endpoint:
Benefit maintained even in LVEF ≥60%
🎯 Finerenone: FINEARTS-HF (September 2024)
6,001 patients with symptomatic HF and LVEF ≥40% across 634 sites in 37 countries
Relative risk reduction in CV death + worsening HF events
RR 0.84 (95% CI 0.74-0.95, p=0.007)
Reduction in worsening HF events alone
RR 0.82 (p=0.007)
Consistent Across LVEF Spectrum (p-interaction 0.75)
RR 0.83
RR 0.79
RR 0.82
Hyperkalemia Profile
K+ >5.5 mmol/L: 14.3% finerenone vs 6.9% placebo (2.6× increase)
Hyperkalemia hospitalizations: 0.5% vs 0.2% (uncommon)
No deaths attributable to hyperkalemia
⚖️ Finerenone vs Steroidal MRAs
Finerenone Advantages
- Non-steroidal structure: no affinity for androgen/progesterone receptors
- Eliminates gynecomastia, breast pain, menstrual irregularities
- Lower hyperkalemia risk (ARTS trial: 5% vs 12% with spironolactone)
- Balanced heart-kidney tissue distribution
TOPCAT Issues
Americas cohort: HR 0.82 (31.8% placebo event rate)
Russia/Georgia: HR 1.10 (8.4% placebo event rate)
2017 NEJM analysis: Canrenone undetectable in large proportions of Eastern European participants
AMBER Trial Comparison
K+ ≥5.5 in CKD with resistant HTN:
Spironolactone without K+ binder: 64.2%
Finerenone (FIDELITY): 11.6%
Part V: Clinical Implementation
🔬 CONFIDENCE Trial (NEJM 2025): Practice-Changing Evidence
First prospective evidence supporting simultaneous finerenone + SGLT2i initiation in diabetic kidney disease
"Finerenone with Empagliflozin in Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes"
N Engl J Med 2025;393:533-43. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2410659
UACR Reduction
with combination therapy at Day 180
Greater Than Finerenone Alone
Additive benefit demonstrated
Greater Than Empagliflozin Alone
Complementary mechanisms
Hyperkalemia with SGLT2i
vs 18.7% without SGLT2i (FIDELITY)
📋 Roundtable Talking Points
1. Safety Signal: SGLT2i co-administration substantially reduces finerenone-associated hyperkalemia through natriuretic and kaliuretic effects.
2. Efficacy Signal: The 52% UACR reduction with combination therapy exceeds what would be expected from simple addition of effects—suggesting synergistic mechanisms.
3. Practical Implications: In patients with stable K+ (<4.5), eGFR ≥45, and significant albuminuria, simultaneous initiation is now evidence-supported.
4. Clinical Integration: This supports the "four-pillar" approach to cardiorenal protection rather than sequential addition of therapies.
🔍 HFpEF Screening in Nephrology Practice
NT-proBNP Thresholds
H2FPEF Score (Simpler Alternative)
| Feature | Points |
|---|---|
| BMI >30 | 2 |
| Multiple antihypertensives (≥2) | 1 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 3 |
| Pulmonary hypertension (PA systolic >35) | 1 |
| Age >60 | 1 |
| Elevated E/e' (>9) | 1 |
Score ≥6: High probability of HFpEF
💊 Finerenone Dosing and Monitoring
Dosing by Baseline eGFR
Critical Monitoring Protocol
4 weeks post-initiation: K+ and eGFR (mandatory)
Uptitrate if: K+ ≤4.8 mEq/L with stable eGFR
Ongoing: Every 4 months
If K+ >5.5 mEq/L:
Hold finerenone until K+ ≤5.0, then restart at lower dose. Consider potassium binders (patiromer, SZC) for recurrent hyperkalemia.
Part VI: Roundtable Question Responses
CKM syndrome (AHA 2023) formalizes the pathophysiological interconnections nephrologists observe clinically. The staging system (0-4) provides actionable structure:
- Stage 2 (metabolic risk or moderate-to-high-risk CKD) → SGLT2i initiation
- Stage 3 (subclinical CVD or eGFR <30) → Add finerenone if UACR >30 on ACEi/ARB
Prioritization follows KDIGO 2024: Optimize RAASi → Add SGLT2i (eGFR ≥20) → Add finerenone if persistent albuminuria (UACR ≥30, eGFR ≥25, K+ ≤5.0) → Consider GLP-1 RA.
Yes. The ADA 2024 Standards now recommend screening for asymptomatic HF in diabetes using BNP or NT-proBNP.
Practical approach: Annual NT-proBNP in all T2D + CKD patients. NT-proBNP ≥125 pg/mL (≥200 if eGFR <45) triggers echocardiography. Early detection enables SGLT2i initiation before symptomatic HF develops.
Key stat: FIGARO demonstrated 32% new-onset HF reduction with finerenone in patients without baseline HF.
The "smoke detector" analogy: "UACR functions as an early warning system for your kidneys and heart—like a smoke detector that detects damage before it becomes irreversible."
Quantify risk: "Your UACR >300 mg/g increases heart failure risk by 1.7-2.7 times—but this is modifiable with treatment."
Set concrete goals: "We're targeting at least 30% UACR reduction."
Connect to outcomes: "TOPCAT showed that 50% UACR reduction correlates with 30-70% lower heart failure hospitalization risk."
CONFIDENCE (NEJM 2025) provides first prospective evidence supporting simultaneous initiation: finerenone + empagliflozin achieved 52% UACR reduction (29% greater than finerenone alone) with similar safety.
My algorithm:
- Simultaneous initiation: Stable patients with high albuminuria, K+ <4.5, eGFR ≥45
- Sequential initiation: Borderline K+ (4.5-4.8), uncertain volume status, or eGFR <45 → SGLT2i first, reassess K+ at 4 weeks, then add finerenone
Key safety finding: SGLT2i co-administration reduces finerenone hyperkalemia (8.1% vs 18.7%).
FINEARTS-HF (September 2024, n=6,001) demonstrated finerenone reduced CV death + worsening HF events by 16% (RR 0.84, p=0.007) in symptomatic HF with LVEF ≥40%.
Remarkably consistent across LVEF spectrum (p-interaction 0.75):
- HFmrEF (LVEF <50%): RR 0.83
- LVEF 50-60%: RR 0.79
- True HFpEF (LVEF >60%): RR 0.82
This addresses concerns from TOPCAT about heterogeneous MRA effects in HFpEF. FDA expanded finerenone indication (July 2025) to include HF with LVEF ≥40%.
🎯 Key Clinical Pearls
❤️🫘 Comprehensive Cardiorenal Disease Evidence Synthesis
Complete evidence-based analysis of modern guideline-directed medical therapy for cardiorenal disease
📄 Comprehensive Cardiorenal Report
31 pages | 82 references | Complete RAAS inhibitor hierarchy, four-pillar GDMT evidence, population health impact analysis
📄 Heart Failure Neurohormonal Report
27 pages | 30 references | MRA phenotype specificity, natriuretic peptide resistance, therapeutic strategies
🎯 Key Evidence Highlights
- RAAS Inhibitor Hierarchy in Heart Failure: ARNIs > ACE-I > ARBs for HF mortality (NNT 36, 70, 446 respectively)
- ACE-I Benefits: Mortality reduction attenuated when combined with comprehensive GDMT (beta-blockers, MRAs, SGLT2i)
- MRA Phenotype Specificity: 2024 Lancet meta-analysis on steroidal vs non-steroidal selection
- CONFIDENCE Trial: 52% UACR reduction with simultaneous SGLT2i + finerenone initiation
- Population Impact: 253 lives saved per 100K annually, $39.4M cost savings, 4.8:1 ROI
- Four-Pillar Synergy: 40-50% mortality reduction with comprehensive GDMT
Document prepared for Bayer-sponsored HFpEF Roundtable Discussion
December 2025